In this section you will learn about post-natal contraception.
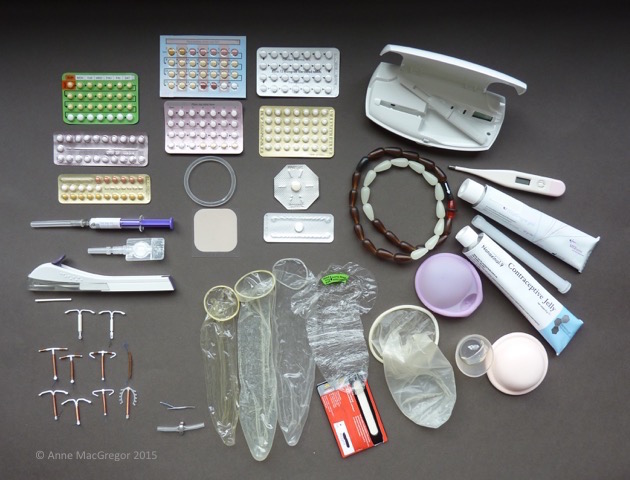

Fertility returns very quickly following childbirth and sexual activity often restarts before the need for contraception is considered or appreciated.
There may be concerns following childbirth about restarting sex and there may be a mismatch in desire and expectations. There is no recommended time to resume sexual activity and some couples will restart very quickly post-delivery and some will need more time to recover.
Some women are anxious about whether sex will be painful in addition to the tiredness and stress of having a small baby, which may then affect the relationship with the partner causing conflict or breakdown in communication. Encouraging couples to discuss the concerns and to explore how to relax, or use lubrication or address the issue appropriately will help.
The GP postnatal check is usually performed when the baby is between 6 and 8 weeks old. This is too late to provide contraception for many women as fertility returns as early as day 24 post-delivery in those who are bottle feeding or breast feeding and supplementing. There are many opportunities to discuss contraception requirements before the formal postnatal check but these are often missed because of all the other postnatal pressures.
Stop and Reflect:
- What myths and concerns do you know that women have about resuming sexual activity or concerns about contraception post childbirth?
- Reflect on your thoughts of supporting women to plan another pregnancy and any opportunities you might have for these discussions?
There are many myths and incorrect concerns about postnatal contraception which should be dispelled including:
- None is required until after the woman has started having periods again.
- Withdrawal is a reliable method of contraception
- Contraception affects breast feeding and baby development
Support and signposting can help women and their partners appreciate the need for use of contraception, the different methods available and where this can be obtained.
Fertility awareness methods rely on the detection of signs and symptoms of fertility and ovulation which may be difficult to assess after child birth, especially in women who are breastfeeding and have not resumed regular menstruation.
Using condoms or the progestogen only pill is a great option while waiting for an appointment to discuss other methods of contraception.
| When can I start contraception | What type of contraception | |
| Immediately | Male or female condoms Contraceptive implant Progestogen-only pill Contraceptive injection | |
| After 3 weeks if not breast feeding or after 6 weeks if breastfeeding or other risk factors such as obesity | Combined pill Combined patch Combined ring | |
| Immediately at delivery or after 4 weeks | Intra-uterine device Intra-uterine system | |
| After 6 weeks | Diaphragm or cap If breastfeeding – combined pill, combined patch, combined ring |
See Also: Resources for information on postnatal health and wellbeing, including advice about contraceptive choices, are available for patients from:
- For Patients:
- For clinicians from the Faculty of Sexual and Reproductive Health






