Introduce
Implementing positive behaviour support strategies helps address challenges while creating safe and nurturing environments for children to thrive. Practitioners should dedicate as much—if not more—time and attention to promoting positive behaviour as they do to managing challenges.
- Set clear expectations
- Model positive behaviours
- Be consistent
- Acknowledge positive efforts
- Evaluate what is effective when supporting behaviour

Develop
The Hand Model of the Brain
Understanding how a child’s brain works can give helpful insight when promoting positive behaviour. What does this video tell us about what might be going on for a child and how we could respond when a child might be expressing big feelings?
When a child is dysregulated, their behaviour might become harder to contain. The following flow chart reminds us of the importance of relationship and connection when managing behaviour. This gives a child an experience of co-regulation, which they need before learning how to self-regulate.
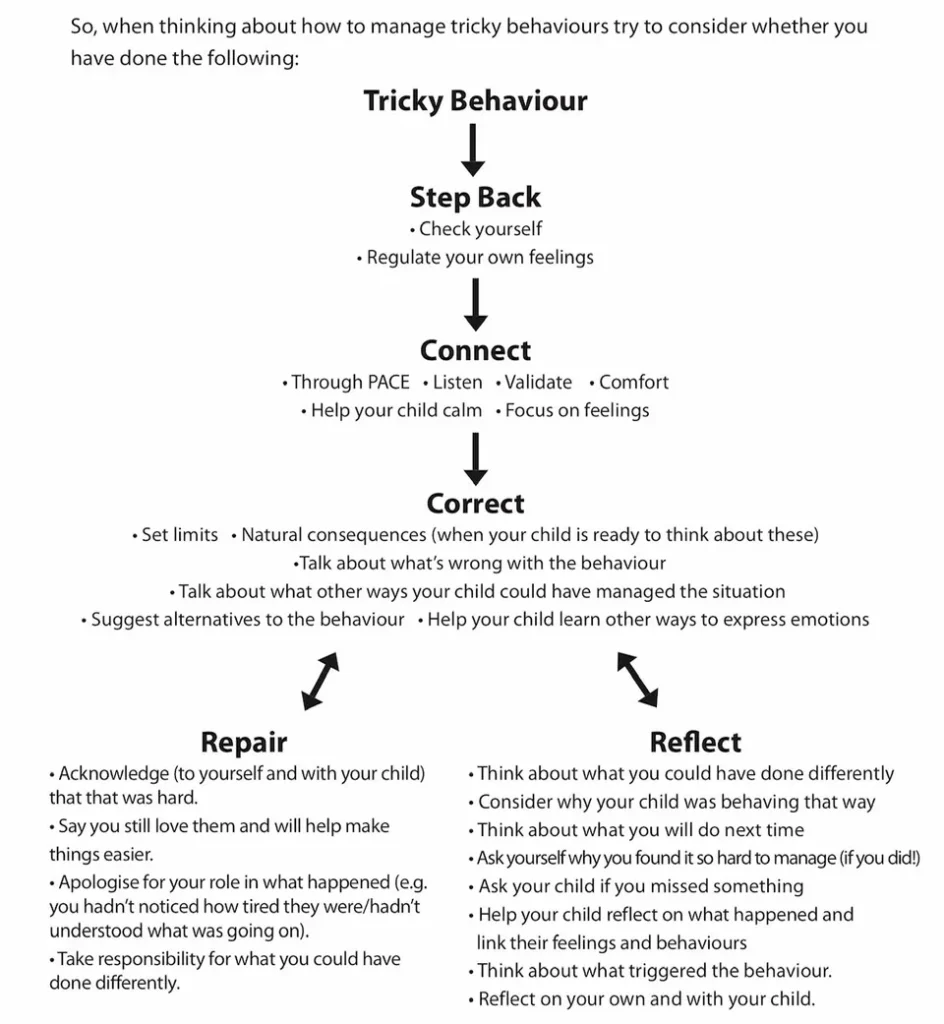
Source: Mundy, S (2020) Parenting Handbook: Helping you and your child make sense of everyday challenges together, Parenting Through Stories.
Reflect
Stop and Reflect: Take some time to think about how you respond to and manage challenging behaviour. Ask yourself the following questions:
– Can you think of a time when you have managed the challenging behaviour of a child? This could be in a work situation or caring for a sibling or child.
– How might you have responded differently to the behaviour by shifting the focus and considering the need behind the behaviour?
– How did you manage the situation? What might have been going on under the surface? What might the child have been trying to communicate?
Optional
The following webinar explores managing challenging behaviours in early years settings, in further depth:






