This blog post was written by me (Tanvir Ahmed) as part of a research internship in which I supported the evaluative work done by researchers in the Decent Work and Productivity Research Centre at Manchester Metropolitan University, regarding a project funded by the Office for Students (OFS) Challenge Competition called Graduates for a Greater Manchester, which aims to contribute to the development of digital skills of students in the city region.
Introduction
The purpose of this summary is to outline the key aspects from a review conducted by researchers in the Decent Work and Productivity Research Centre. The summary will focus on the main topics outlined in the report, the local graduate labour market regarding skills shortages and supply and demand for tech and creative digital skills within Greater Manchester. This summary will be useful to students, graduates, and others within a professional field by giving them a better outlook on the graduate labour market of Greater Manchester, which includes skills in demand which can be acquired to increase employability and the underemployment of graduates.
What do we mean by ‘Tech’ and ‘Creative ‘Digital sectors?
T and CD sectors also known as ‘Tech’ and ‘Creative’ ‘Digital’. The ‘Tech’ and ‘Creative’ are sectors that are being influenced by digital change. Digital transformation is having an influence on job roles across all industries. The trend can be described using the word digital: ‘creative digital’ which is the digital transformation of creative production, distribution, and consumption, ‘tech digital’ which is the transformation of technology industry processes.
Definition of Creative Sector:
| Box 1: DCMS Creative Industries (2018) Advertising and marketingArchitecture Crafts Product design, graphic design, and fashion designFilm, TV, video, radio, and photographyIT, software, video games and computer servicesPublishing and transition Museums, galleries, and libraries Music, performing arts, visual arts, and cultural education |
| Box 2: Tech Nation, digital tech industries (2018) Manufacture of computers and peripheral equipmentPublishing of computer gamesOther software publishingWired telecommunications Wireless telecommunicationsSatellite telecommunications Other telecommunications Computer programming activities Computer consultancy activities Computer facilities management activitiesOther IT & computer service activities Data processing, hosting & related activitiesWeb portals Repair of computers & peripheral equipment |
What do graduates of the North West do?
Across many industries the North West finds itself facing shortages of suitably skilled graduate candidates. Despite shortages in tech and creative digital, findings reveal the region struggles to fill vacancies in sales more than any other sector along with roles such as accountants, nurses, housing, recruitment, youth workers. However, shortages can also depend on employment demand, for example business services roles may face shortages due to the rapid expansion of business-oriented jobs.
Nevertheless, the North West does well in retaining graduates, 69.4% of graduates start work in the region six months after graduating from a higher education institution, many working in fields that suffer from a shortage of suitably qualified graduates.
Figure 1: Occupations for graduates in North West (Prospects, 2019b)
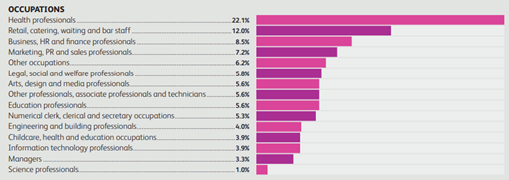
The tech and creative digital sectors have experienced an increasing growth of opportunities over the years, however the demand for tech savvy graduates is demanded across most industries. It highlights the role higher education has in equipping graduates with up-to-date skills regardless of the industry they move into, partners of the ‘Graduates for a Greater Manchester’ project is an example of an initiative to equip and enhance the digital skills of not only those working in tech and creative digital but across all sectors.
The ‘Digital and Creative’ sector of Manchester and mainly Salford/MediaCityUK due to its internationally present ‘Digital and Creative’ activities has a huge impact on the growth and opportunities which includes health innovation, clean growth, advance materials, and manufacturing and ‘Digital and Creative’ media.
Opportunities are on the rise but the misalignment between the education providers and sector requirements in Digital and Creative, Business and Professional Services remains an issue. However, policies by the Local Industrial Strategy have been put in place in upskilling the workforce, universities and the education provided is a key feature. Which aligns well with the ‘Graduates for a Greater Manchester’ commitment in ensuring a qualified workforce that meet high tech and digital industry requirements. The Prosperity review highlights the link between skills and productivity, and though GM has experienced significant growth over years its skill levels lag behind on a national scale.
Is there a shortage of T and CD graduates in Greater Manchester?
Shortage of skills in Greater Manchester is an issue. Findings revealed that 70% of businesses hired graduates however only 13% believed that the graduates hired had the correct soft skills and technical knowledge to be work ready. The majority of respondents felt as though the industry did not intervene enough in the education sector to help prepare young people for tech and digital careers. This is an issue founded within members of the Institute of Student Employers who face staff shortages within analytical, IT programming and engineering roles. Since then higher-level apprenticeships is an intervention implemented in the education to address the skills shortages in T and CD sectors.
The New Economy shows another perspective of the skills supply/shortage of GM. Their analysis reveals that the number of people with a level 4 qualification has risen a lot faster than the number of jobs with level 4 requirements, which highlights that unemployment and underemployment are both issues within the GM labour market.
Figure 4: Level 4 Skills and Jobs – Source, New Economy, 2017
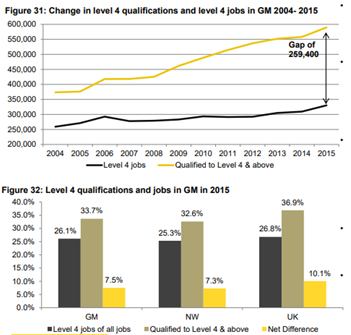
Nevertheless, a wide-ranging higher skill set is what Universities UK argue to be needed for a future of lifelong learning. Digital skills are needed across all industries not specifically to just the tech and creative digital sectors. As digitalisation become the future for most industries it highlights the importance for T and CD skills in non-specialist graduates entering non- T and CD roles.
Conclusion:
The ‘Tech’ ‘Creative’ ‘Digital’ are evolving sectors expected to have immense potential. These sectors are key to economic growth in Greater Manchester and therefore must be supported in effective ways. Higher education institutions are vital when it comes to supporting the enhancement of digital skills among their students/graduates, this will help address the digital skill shortages Greater Manchester faces. These changes must also take place for non-specialist graduates as the requirement for them to have acquired T and CD skills will also be in demand despite entering into non-T and CD industries. Other changes needing to be made which involves graduate under-employment and under-utilisation of graduate skills. The Graduates for Greater Manchester programme is a good start with its involvement with employers and other stakeholders, just as much as universities, employers are a key part of change, by providing opportunities for staff training and progression will allow them to use graduate skills effectively.
Digital skills should now be part of the wider skill set of each individual no matter the industry they enter, as digitalisation is the future. Universities and employers working closely together will help reach students effectively about the career routes they can take and opportunities acquiring digital skills can bring which will spark the motivation most lack.






